Heat Transfer Solutions
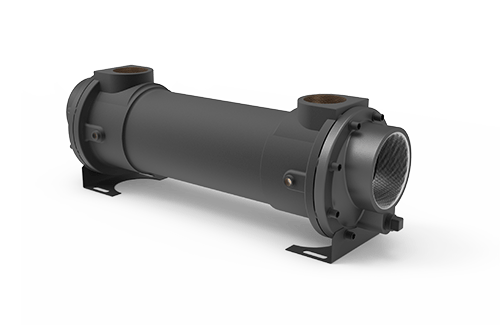
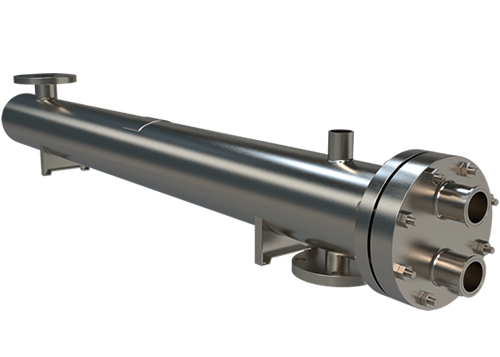
A shell and tube heat exchanger is a type of heat transfer device that can be used to efficiently transfer thermal energy from one medium to another. In these types of systems, the heat exchange takes place between two fluids contained inside a shell with multiple tubes running through it. The shell contains the first fluid which is then circulated around the multiple tubes. The second fluid is circulated through the tubes where it absorbs heat from the shell and transfers it to its destination. Heat exchangers are designed to be efficient at transferring thermal energy, making them ideal for applications such as refrigeration, engine cooling or power plant systems.
Shell and tube exchangers come in many variations to meet process requirements in almost every industry or application. They deliver reliable heat transfer performance by utilizing a high turbulence and counter flow, making one or more passes. While one (1), two (2) and four (4) pass models are standard, multi-pass custom models of any size are available.
If you have questions about how a shell and tube exchanger will benefit your application, or would like a quote please contact us: 1-805-484-2992
Materials & Construction
By combining suitable materials with well-thought-out design principles, shell and tube heat exchangers can achieve optimal performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness tailored to specific industrial requirements.
- Thermal Conductivity: Materials such as copper and brass are chosen for their superior thermal conductivity, making them ideal for efficient heat transfer.
- Corrosion Resistance: 316 and 304 stainless steels, as well as nickel and titanium, are utilized for their excellent resistance to corrosion and high temperatures, particularly in aggressive environments.
- Configuration Variety: Exchanger designs are often one-pass, two-pass, or four-pass, which dictate how fluids flow through the system and impact heat transfer rates.
- Application-Specific Materials: CuNi (Copper-Nickel) is favored for seawater applications due to its resilience in saline conditions, and carbon steel is selected for its optimal balance of strength and cost-effectiveness in less corrosive environments.
- Efficiency Optimization: The design focuses on maximizing heat transfer efficiency while ensuring structural integrity. This involves careful consideration of factors like tube length, diameter, and fluid flow paths.
- Tube Bundle Design: Tube bundles can be fixed or removable, with varying configurations such as straight tube for ease of maintenance and reduced pressure drops, or U-tube for accommodating thermal expansion without inducing stress on tube joints.